Configure Service Model
This section describes the Service Model (also referred to as the CMDB) and how to configure it. Configuration of the Service Data Model is optional.
Note: Before you configure the Service Model you must configure all the RTView DataServers you wish to include in your RTView Enterprise deployment.
To configure the CMDB you associate each CI in your system with a Service, Group, Area and Owner. These associations form the map that enables aggregation of data in RTView Enterprise Service displays. There are several ways to create the CMDB:
| • | Manually, using the RTView Configuration Application and the Administration - CMDB Admin display. See Configuration Steps . |
| • | Import an existing structure from a spreadsheet or database. |
| • | If the data is available to the Configuration Server, you can read it dynamically by populating the structure from the raw data. |
| • | Any combination of the above. |
This section contains:
| • | Introduction to the CMDB: Describes the CMDB structure, and provides examples of how an organization's established structure can be applied to the CMDB. |
| • | Configuration Steps : Step-by-step CMDB configuration instructions. |
Introduction to the CMDB
This section describes the RTView Enterprise Service Model and its configuration. Before the CMDB is configured, your solution package data is only visible in displays that are specifically for that solution package (such as the displays in the Components tab).
After you configure the CMDB, you gain a "single-pane-of-glass" view. That is, your solution package data is visible and incorporated into the displays and performance metrics of all relevant displays (such as displays under the Services tab).
The CMDB is a database containing the master hierarchical map of associations between all component IDs (CIs), Services, Groups, Areas and Owners in your system. A CI is an item in your system that is being monitored by RTView Enterprise. The item could be an application, a cache, a server, a router, a NIC card, a server partition, a connection and so forth.
The CMDB contains four hierarchical levels that should suit the monitoring needs of most organizations. The four levels are, from the highest level (Owner) to the lowest level (Service):
| • | Owner |
| • | Area |
| • | Group |
| • | Service |
The names of the CMDB levels cannot be modified.
When you configure your CMDB you associate each CI in your system with a Service, each Service with a Group, each Group with an Area and each Area with an Owner. These associations form the map that enables aggregation of data in RTViewCentral displays. There is no limit on the number of associations a level can have. A Service can be associated with multiple Groups and Environments.
When you make any changes to Owners, Areas, Groups or Services the associated levels are automatically updated. For example, when you move a Group from one Area to another, all Services associated with that Group move with it, and the RTViewCentral displays are updated.
By default, the CMDB contains a single Owner named Infrastructure which organizes the CI’s by Solution Package.Infrastructure cannot be modified, but it can be disabled in the Service Model Page of the RTView Configuration Application.
Defining the CMDB
When you configure the Service Data Model you use the existing structure of your organization to do so. If your organization does not have an established structure, you need to define one relevant to your system. The manner in which you adapt your system hierarchy to the CMDB levels depends on the monitoring needs of your organization. You design the CMDB by identifying the four hierarchical levels in your organization that coincide with the four-level hierarchy in the CMDB. For example, you might:
| 1. | Determine the Owners: Note the person or persons responsible for alerts in your organization. You might have only one Owner. |
| 2. | Determine the Areas for each Owner: The Areas are relevant to the Owner accountable for resources in the Areas. Areas might be based on departments in the organization (such as Development, Sales, HR, and so forth). |
| 3. | Determine the Groups for each Area: Groups might be comprised of, for example, the types of resources used in the Areas (such as Servers, Middleware and Processes). |
| 4. | Determine the Services for each Group: Services might be comprised of a variety of applications that are used by a given Group. |
After you determine how to adapt your organization to the four levels of the CMDB, use the Administration -CMDB Admin display to map each CI to a Service, Group, Area and Owner. The name of the CI can indicate which Service you want to associate the CI with.
The CMDB automatically classifies the CIs in your system into CI Types. This classification is based on a preconfigured schema that is internal to RTView Enterprise. CI Types are determined by the role of a given CI, and the name of the CI Type describes the role. For example, a BusinessWorks application process is a BW-PROCESS CI Type, a BusinessWorks server is a BW-SERVER CI Type and an Oracle database is an ORACLE CI Type.
After you configure a Service Data Model, the automatically generated Infrastructure Service Data Model looks for matching CI's in your Service Data Model in order to set the Environment. For each CI in the automatically generated Infrastructure Service Data Model, if a matching CI is found in your Service Data Model, the Environment from your Service Data Model is used for the Infrastructure CI. If the CI is found in your Service Data Model multiple times with multiple Environments, it is added multiple times to the Infrastructure CMDB--once for each Environment in your Service Data Model for that CI. If no matching CI is found in your Service Data Model, the Environment in the Infrastructure Service Data Model is set to PRODUCTION by default. You can override the default Environment by specifying a different environment in the Service Model Page/ Default Environment Filter field.
Configuration Steps
This section describes how to configure the Service Model using the RTView Configuration Application and the RTView EnterpriseAdmin tab/ CMDB Admin display.
This section assumes you configured the CMDB database connection. If not, see Configure RTViewCentral Databases.
| 1. | Open the RTView Configuration Application, go to Server Configuration/Service Model and: |
| • | Toggle on Read Service Model from Database to organize CIs in COMPONENTS displays. |
| • | Toggle on Organize Services by CIType if you want to include CIs in Infrastructure Owner displays (recommended). |
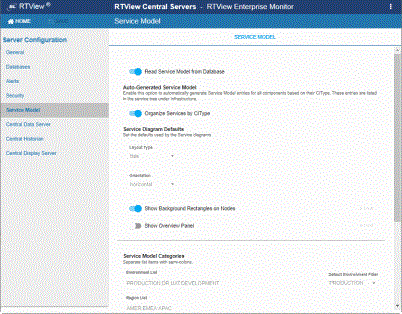
| 2. | Under Service Model Categories, enter category names in a semi-colon separated list format for each field. Optionally, change the Default Environment Filter. |
| 3. | Click  to apply them. to apply them. |
Start RTViewCentral and go to the Admin tab/ CMDB Admin display:
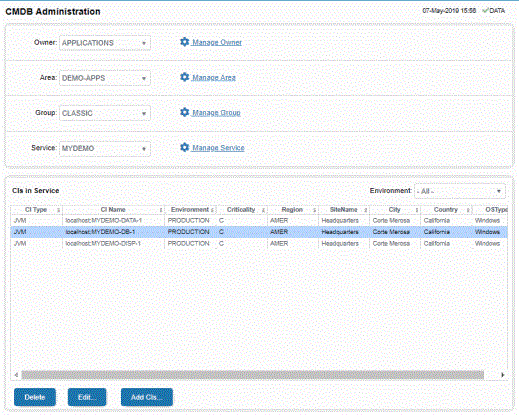
See the following instructions to:
| • | Add CIs to the CMDB |
| • | Delete a CI |
| • | Edit CI Properties |
| • | Create, Delete, Rename or Merge Owners, Areas, Groups or Services |
| • | Move a Service, Group or Area |
Add CIs to the CMDB
You add CIs to the CMDB by associating them with a Service. CIs can be associated with more than one Service.
To add CIs to the CMDB:
| 1. | Click  to open the Find CIs to add table which contains all CIs that are available in your RTView Enterprise system (regardless of whether they are already in the CMDB). to open the Find CIs to add table which contains all CIs that are available in your RTView Enterprise system (regardless of whether they are already in the CMDB). |
| 2. | Select one or more CIs in the Find CIs to add table and Set CI properties (including Criticality) using the drop-down menus. You can filter the list using the CI Type drop-down or by entering a search string in CI Name Filter. |
| 3. | Choose the Service you want to add the CI(s) to. You can: |
| • | add the CI(s) to an existing Service by selecting it from the Service drop-down (at the top of the display) and clicking  . . |
| • | add the CI(s) to a new Service you create by entering a New Owner Name, New Area Name, New Group Name and a New Service Name, and clicking  . . |
The CI(s) are now listed in the CIs in Service table.
It is not necessary to restart the Configuration Server after making changes to the Service Data Model using the CMDB Admin display.
Delete a CI
Select one or more CIs in the CIs in Service table, then click  . The CI is removed from the CMDB database and displays. Your changes are immediately visible in the drop-down menus and displays.
. The CI is removed from the CMDB database and displays. Your changes are immediately visible in the drop-down menus and displays.
There is no option to undo a deletion from the CMDB. To restore a deletion you must find the CI again and re-associate it with the Service.
And when you delete all CIs from the list, the Service is also removed from the CMDB. A given Service can only exist if it contains one or more CIs. If the Service no longer exists as a result of removing the last of its CIs, you must also recreate the Service (by typing the names of the Owner, Area, Group, and Service).
Edit CI Properties
Select one or more CIs in the CIs in Service table, then click  . Use the drop-down menus to modify settings, then click
. Use the drop-down menus to modify settings, then click  . Your changes are immediately visible in the drop-down menus and displays.
. Your changes are immediately visible in the drop-down menus and displays.
Criticality is the importance level of a CI to your organization. Criticality values range from A to E, where A is the highest Criticality and E is the lowest Criticality (with equally spaced intermediate values). This value is used to calculate Alert Impact (the maximum Alert Severity multiplied by the maximum Criticality equals Alert Impact).
Criticality values are listed in the Component Views - CI Service Table display. Criticality values are also shown in heatmaps and tables.
Create, Delete, Rename or Merge Owners, Areas, Groups or Services
You can create, delete and rename the Owners, Areas, Groups and Services. To illustrate, we use Owner as an example.
Select the Owner you want to modify and click the  (Manage cogwheel icon) next to it. You can:
(Manage cogwheel icon) next to it. You can:
| • | Delete the Owner by clicking  . . |
This removes the Owner and all CI associations from the CMDB.
| • | Rename the Owner by entering a New Owner Name and clicking  . . |
This changes the name of the Owner, creates a new Owner and retains all CI associations in the CMDB under the new Owner name.
| • | Create an Owner by clicking  to open the Find CIs to add table, then select one or more CIs in the CIs in Service table and enter the new Owner name in the New Owner Name field. Enter either an existing name or new name for the Area, Group and Service fields. Then click Add to New Service or Add to Existing Service. to open the Find CIs to add table, then select one or more CIs in the CIs in Service table and enter the new Owner name in the New Owner Name field. Enter either an existing name or new name for the Area, Group and Service fields. Then click Add to New Service or Add to Existing Service. |
| • | Merge all CIs under an Owner with another existing Owner by entering the existing target Owner in the New Owner Name field and clicking Merge With Existing Owner. |
This changes the Owner name to that of the target Owner’s name and moves all lower level CMDB associations (Services, Groups and Areas and associated CIs) go with it. For example, let’s say Owner A is associated with one Area, that Area is associated with two different Groups, and both of those Groups are associated with two different Services. When you merge Owner A with Owner B, Owner B becomes the Owner of that one Area, the two Groups, the four Services and all the CIs associated with them.
This option is useful when, for example, an existing Owner is taking over for a retiring Owner.
Move a Service, Group or Area
When you move a Service, Group or Area (Owners cannot be moved) you move it up one level in the CMDB and all lower level CMDB associations (Services, Groups and Areas and associated CIs) go with it.
This option is useful when, for example, it makes more organizational sense to have an Area under a different Owner, a Group under a different Area or a Service under a different Group. To illustrate, we use Group as an example.
Select the Group that you want to move to another Group and click the  (ManageGroup cogwheel icon) next to it. You can:
(ManageGroup cogwheel icon) next to it. You can:
| • | Move all CIs to another Area by selecting the target Owner and Area that you want to move the Group to and clicking  . . |
This changes the name of the Owner and Area and retains all CI associations in the CMDB under the new Owner and Area.
| • | Move all CIs to New Area by typing the New Owner Name and New Area Name that you want to move the Group to and clicking  . . |
This changes the name of the Owner and Area, creates a new Owner and Area and retains all CI associations in the CMDB under the new Owner and Area.