
These displays provide detailed data and statuses for CSPF neighbor brokers. You can check trends on network traffic among CSPF neighbors. Note that these displays are empty if you are only monitoring Solace Cloud PubSub+ Brokers. Displays in this View are:
Neighbors Table: View metrics for Solace neighbor brokers that use the Content Shortest Path First (CSPF) routing protocol to determine the shortest path in which to send messages from one broker to another broker in the Solace network.
CSPF Neighbors Diagram: Topological view of CSPF Neighbors that shows broker connections and status of servers (Active/Inactive).
Neighbors Summary: View detailed performance metrics for a single Solace neighbor broker that uses the CSPF routing protocol.
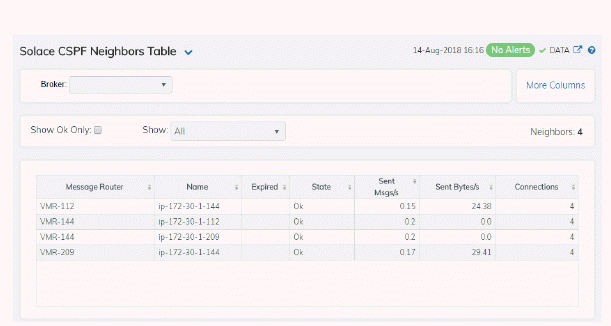
This tabular display shows Content Shortest Path First (CSPF) neighbor metrics for a broker. Each row in the table is a neighbor link. Select a broker from the drop-down menu. View metrics for a Solace neighbor broker that uses the CSPF routing protocol to determine the least cost path in which to send messages from one broker to another broker in the Solace network.
Search by clicking the right side of a column heading/Filter to open the Search, Sort and Choose Columns dialog:

By default, a subset of available metrics is shown. Use More Columns/Less Columns to toggle to the complete set of metrics available (and back to the subset).
|
|
Neighbor Count: |
The number of neighbor brokers connected to the selected Broker. |
||
|
|
Show: |
OK |
Select to only show neighbor brokers that are connected (State is OK). By default, this option is not selected (all neighbor brokers are shown. |
|
|
|
|
Expired |
Select to show both expired and non-expired neighbor brokers. By default, this option is not selected (only non-expired neighbor brokers are shown). |
|
|
Table: Each table row is a different neighbor broker. |
||||
|
|
Broker |
The name of the neighbor broker. |
||
|
|
State |
The current state of the neighbor link. |
||
|
|
Up Time |
The amount of time the broker has been up and running. |
||
|
|
Connections |
The number of connections. |
||
|
|
Link Cost Actual |
Refer to Solace documentation for more information. |
||
|
|
Link Cost Configured |
Refer to Solace documentation for more information. |
||
|
|
Data Port |
Refer to Solace documentation for more information. |
||
|
|
Expired |
When checked, performance data about the broker has not been received within the time specified. |
||
|
|
Timestamp |
The date and time the row of data was last updated. |
||
Use this topology display to monitor the health of network components: Solace brokers, VMRs, servers and neighbor links. Quickly identify broker neighbors that are inactive and which resources their performance impacts.
Each node in the display is a Solace broker, VMR or server. If the value of the node's Connected column is true, then the node is green. If the value in its Expired column is true, it is dark gray. Otherwise the node is not connected and not expired, and the color is light gray.
 shows the number of current alerts associated with the objects and uses the following color code:
shows the number of current alerts associated with the objects and uses the following color code:
 Red indicates that there are one or more alerts in a critical state.
Red indicates that there are one or more alerts in a critical state.
 Yellow indicates that there are one or more one or more alerts in a warning state.
Yellow indicates that there are one or more one or more alerts in a warning state.
 Green indicates that there are no alerts.
Green indicates that there are no alerts.
The lines connecting nodes represent neighbor links. If the value of the neighbor link State, is OK (which is shown in the Neighbors Table), then the neighbor link is green and if not the neighbor link yellow.
Drag and drop objects to arrange them on the screen (doing so does not logically impact Solace brokers, software or servers).
This display only shows items that are categorized as Appliance, Appliance-Pair, VPN, ApplianceCapacity, Client, Bridge or Endpoint. And when you click  to open the Alerts Table by Component display and investigate alerts, only alerts for items in these categories are listed.
to open the Alerts Table by Component display and investigate alerts, only alerts for items in these categories are listed.
You can mouse-over objects to see their Host IP address and Platform. Right-click on VMR objects and select Open VMR UI to open the Solace VMR login web page. Double-click to drill down and investigate in the Neighbors Table.
(Please scroll down for details about using the tool bar.)
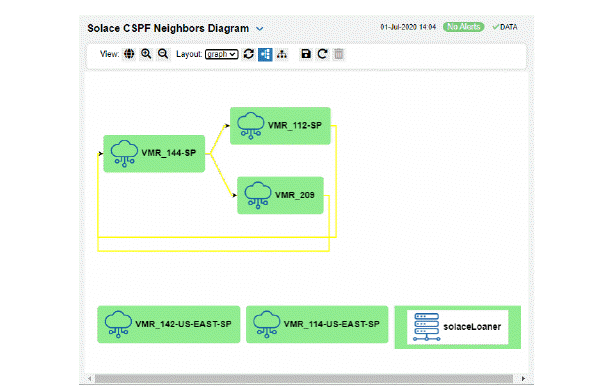
Use the tool bar to interact with the diagram:
 - Toggle to include/exclude the overview (a thumbnail version of display elements that appears in the upper left margin of the display).
- Toggle to include/exclude the overview (a thumbnail version of display elements that appears in the upper left margin of the display).
 - Zoom In/Zoom Out
- Zoom In/Zoom Out
 - Apply the selected layout options. This is useful to restore the layout after clicking and dragging the nodes or while adding links.
- Apply the selected layout options. This is useful to restore the layout after clicking and dragging the nodes or while adding links.
 - Apply a vertical flow/horizontal flow (these options apply to tree and graph layout only).
- Apply a vertical flow/horizontal flow (these options apply to tree and graph layout only).
 - Save the layout options including the positions of any manually moved nodes to the local browser storage. This will be used instead of the default layout whenever you view this diagram in the browser where it was saved.
- Save the layout options including the positions of any manually moved nodes to the local browser storage. This will be used instead of the default layout whenever you view this diagram in the browser where it was saved.
 - Restore the layout options in the toolbar to the locally saved layout if there is one, otherwise to the default layout.
- Restore the layout options in the toolbar to the locally saved layout if there is one, otherwise to the default layout.
 - Delete the locally saved layout options.
- Delete the locally saved layout options.
You can select a layout type to apply to the diagram. You can also click and drag the component nodes to lay them out manually.

The tree and graph layouts are useful on diagrams where the flow (links) between nodes go mostly in one direction, from one or more root nodes to child nodes, then to grandchild nodes, and so forth. The graph layout attempts to keep the nodes arranged neatly in rows or columns, the tree layout places the nodes more closely together.
The net layout can be useful for diagrams where the flow between nodes goes in multiple directions.
The circle layout can be useful for diagrams where the flow is mostly in one direction but where there are also links from the deepest child nodes back to top level nodes.
To monitor network bridges and VPNs, see the Bridges Diagram.
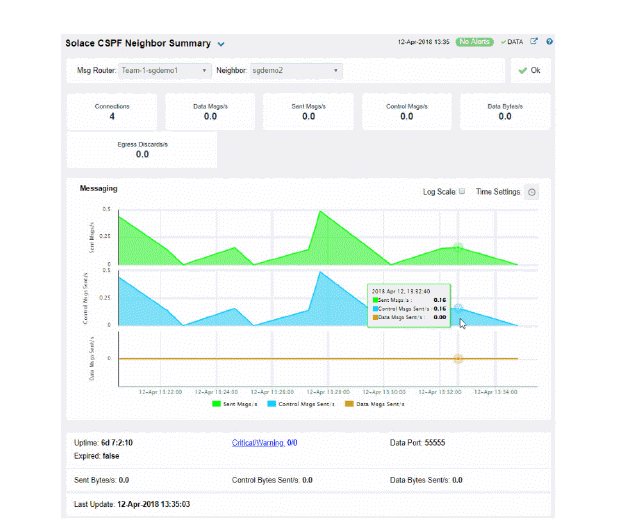
View neighbor broker current configuration details and message throughput rates.
Select a broker and a neighbor broker from the drop down menus. Check message throughput rates to the neighbor broker, as well as neighbor Up Time, State, Data Port, number of connections and link costs.
You can hover over the metric cards to see more performance metrics and also drill down to see even more detail by clicking on them.
The bottom half of the display provides current and historical performance metrics for the selected broker. The trend graph traces the performance metric you select: Message Flow or Throughput.
You can hover over the trend graph to see the values at a particular time. You can specify the time range for the trend graph and view data based on a log scale, which enables visualization on a logarithmic scale and should be used when the range in your data is very broad.
The trend graph traces the current and historical message throughput (Data, Control, Discards and Total).
|
|
Neighbor: |
Select the neighbor broker for which you want to show data in the display. |
||
|
|
Connections |
The current number of connections. |
||
|
|
Data Msgs/s |
Refer to Solace documentation for more information. |
||
|
|
Sent Msgs/s |
Refer to Solace documentation for more information. |
||
|
|
Control Msgs/ s |
Refer to Solace documentation for more information. |
||
|
|
Data Bytes/s |
Refer to Solace documentation for more information. |
||
|
|
Egress Discards/s |
The total number of discarded messages sent from the selected Broker to the selected Neighbor broker since the broker was last started. |
||
|
Trend Graphs Traces the rates of messages sent from the selected Broker to the selected Neighbor broker. |
||||
|
|
Sent Msgs/s |
Refer to Solace documentation for more information. |
||
|
|
Control Msgs/s |
Refer to Solace documentation for more information. |
||
|
|
Discards/s |
Traces the number of discarded messages sent, per second, from the selected Broker to the selected Neighbor broker. |
||
|
|
Log Scale |
Select to enable a logarithmic scale. Use Log Scale to see usage correlations for data with a wide range of values. For example, if a minority of your data is on a scale of tens, and a majority of your data is on a scale of thousands, the minority of your data is typically not visible in non-log scale graphs. Log Scale makes data on both scales visible by applying logarithmic values rather than actual values to the data. |
||
|
|
Time Settings |
By default, the time range end point is the current time. To change the time range, click the Time Settings
Toggle forward/backward in the trend graph per the period you choose (from the Time range drop-down menu) using arrows Restore settings to current time by selecting now
|
||